前言
簡單聊一下cocos2djs手遊的逆向,有任何相關想法歡迎和我討論^^
一些概念
列出一些個人認為比較有用的概念:
- Cocos遊戲的兩大開發工具分別是
CocosCreator和CocosStudio,區別是前者是cocos2djs專用的開發工具,後者則是cocos2d-lua、cocos2d-cpp那些。

- 使用
Cocos Creator 2開發的手遊,生成的關鍵so默認名稱是libcocos2djs.so
- 使用
Cocos Creator 3開發的手遊,生成的關鍵so默認名稱是libcocos.so ( 入口函數非applicationDidFinishLaunching )
- Cocos Creator在構建時可以選擇是否對
.js腳本進行加密&壓縮,而加密算法固定是xxtea,還可以選擇是否使用Zip壓縮 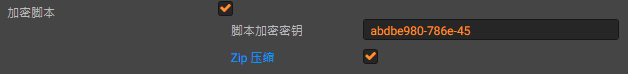
libcocos2djs.so裡的AppDelegate::applicationDidFinishLaunching是入口函數,可以從這裡開始進行分析- Cocos2djs是Cocos2d-x的一個分支,因此https://github.com/cocos2d/cocos2d-x源碼同樣適用於Cocos2djs
自己寫一個Demo
自己寫一個Demo來分析的好處是能夠快速地判斷某個錯誤是由於被檢測到?還是本來就會如此?
版本信息
嘗試過2.4.2、2.4.6兩個版本,都構建失敗,最終成功的版本信息如下:
- 編輯器版本:
Creator 2.4.13 ( 2系列裡的最高版本,低版本在AS編譯時會報一堆錯誤 )
- ndk版本:
23.1.7779620
project/build.gradle:classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:8.0.2'project/gradle/gradle-wrapper.properties:distributionUrl=https\://services.gradle.org/distributions/gradle-8.0.2-all.zip
Cocos Creator基礎用法
由於本人不懂cocos遊戲開發,只好直接用官方的Hello World模板。
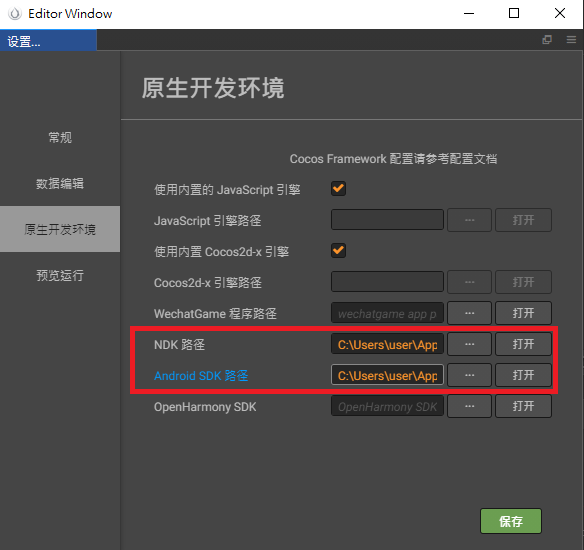
首先要設置SDK和NDK路徑
然後構建的參數設置如下,主要需要設置以下兩點:
- 加密腳本:全都勾上,密鑰用默認的
- Source Map:保留符號,這樣IDA在打開時才能看到函數名
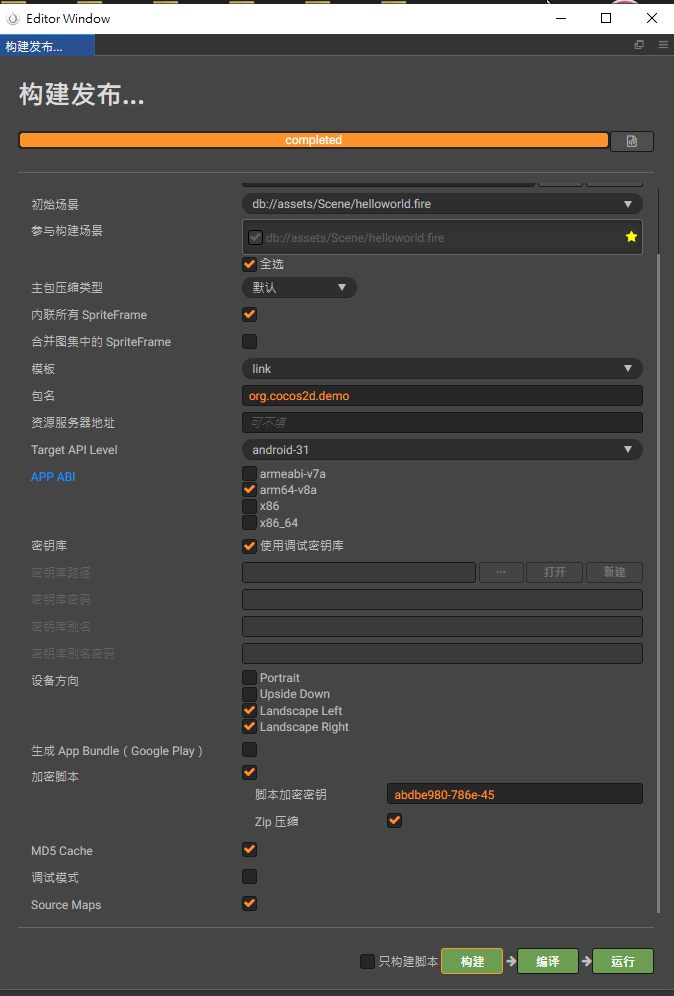
我使用Cocos Creator能順利構建,但無法編譯,只好改用Android Studio來編譯。
使用Android Studio打開build\jsb-link\frameworks\runtime-src\proj.android-studio,然後就可以按正常AS流程進行編譯
Demo如下所示,在中心輸出了Hello, World!。

jsc腳本解密
上述Demo構建中有一個選項是【加密腳本】,它會將js腳本通過xxtea算法加密成.jsc。
而遊戲的一些功能就會通過js腳本來實現,因此cocos2djs逆向首要事件就是將.jsc解密,通常.jsc會存放在apk內的assets目錄下
獲取解密key
方法一:從applicationDidFinishLaunching入手
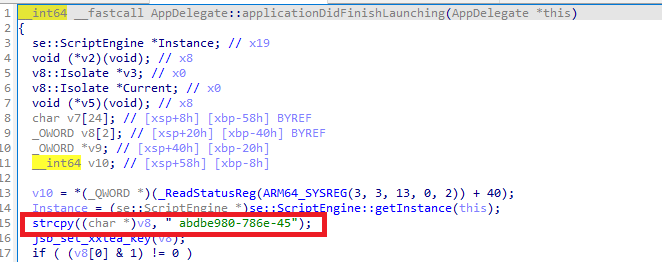
方法二:HOOK
- hook
set_xxtea_key
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
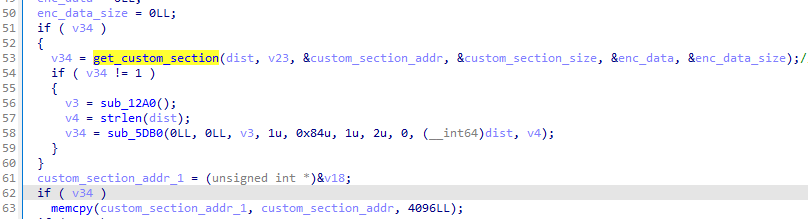
12
|
function hook_jsb_set_xxtea_key(soName) {
let set_xxtea_key = Module.findExportByName(soName, "_Z17jsb_set_xxtea_keyRKNSt6__ndk112basic_stringIcNS_11char_traitsIcEENS_9allocatorIcEEEE");
Interceptor.attach(set_xxtea_key,{
onEnter(args){
console.log("xxtea key: ", args[0].readCString())
},
onLeave(retval){
}
})
}
|
- hook
xxtea_decrypt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| function hook_xxtea_decrypt(soName) {
let set_xxtea_key = Module.findExportByName(soName, "xxtea_decrypt");
Interceptor.attach(set_xxtea_key,{
onEnter(args){
console.log("xxtea key: ", args[2].readCString())
},
onLeave(retval){
}
})
}
|
python加解密腳本
一次性解密output_dir目錄下所有.jsc,並在input_dir生成與output_dir同樣的目錄結構。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
|
import xxtea
import gzip
import jsbeautifier
import os
KEY = "abdbe980-786e-45"
input_dir = r"cocos2djs_demo\assets"
output_dir = r"cocos2djs_demo\output"
def jscDecrypt(data: bytes, needJsBeautifier = True):
dec = xxtea.decrypt(data, KEY)
jscode = gzip.decompress(dec).decode()
if needJsBeautifier:
return jsbeautifier.beautify(jscode)
else:
return jscode
def jscEncrypt(data):
compress_data = gzip.compress(data.encode())
enc = xxtea.encrypt(compress_data, KEY)
return enc
def decryptAll():
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(input_dir):
for dir in dirs:
dir_path = os.path.join(root, dir)
target_dir = output_dir + dir_path.replace(input_dir, "")
if not os.path.exists(target_dir):
os.mkdir(target_dir)
for file in files:
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
if not file.endswith(".jsc"):
continue
with open(file_path, mode = "rb") as f:
enc_jsc = f.read()
dec_jscode = jscDecrypt(enc_jsc)
output_file_path = output_dir + file_path.replace(input_dir, "").replace(".jsc", "") + ".js"
print(output_file_path)
with open(output_file_path, mode = "w", encoding = "utf-8") as f:
f.write(dec_jscode)
def decryptOne(path):
with open(path, mode = "rb") as f:
enc_jsc = f.read()
dec_jscode = jscDecrypt(enc_jsc, False)
output_path = path.split(".jsc")[0] + ".js"
with open(output_path, mode = "w", encoding = "utf-8") as f:
f.write(dec_jscode)
def encryptOne(path):
with open(path, mode = "r", encoding = "utf-8") as f:
jscode = f.read()
enc_data = jscEncrypt(jscode)
output_path = path.split(".js")[0] + ".jsc"
with open(output_path, mode = "wb") as f:
f.write(enc_data)
if __name__ == "__main__":
decryptAll()
|
jsc文件的2種讀取方式
為實現對遊戲正常功能的干涉,顯然需要修改遊戲執行的js腳本。而替換.jsc文件是其中一種思路,前提是要找到讀取.jsc文件的地方。
方式一:從apk裡讀取
我自己編譯的Demo就是以這種方式讀取/data/app/XXX/base.apk裡assets目錄內的.jsc文件。
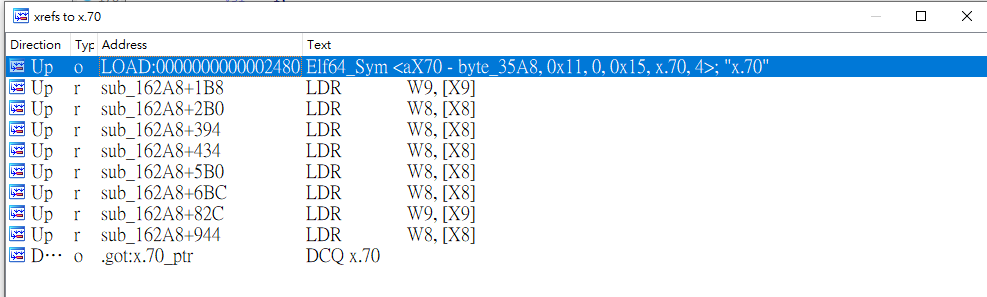
cocos引擎默認使用xxtea算法來對.jsc等腳本進行加密,因此讀取.jsc的操作定然在xxtea_decrypt之前。
跟cocos2d-x源碼,找使用xxtea_decrypt的地方,可以定位到LuaStack::luaLoadChunksFromZIP
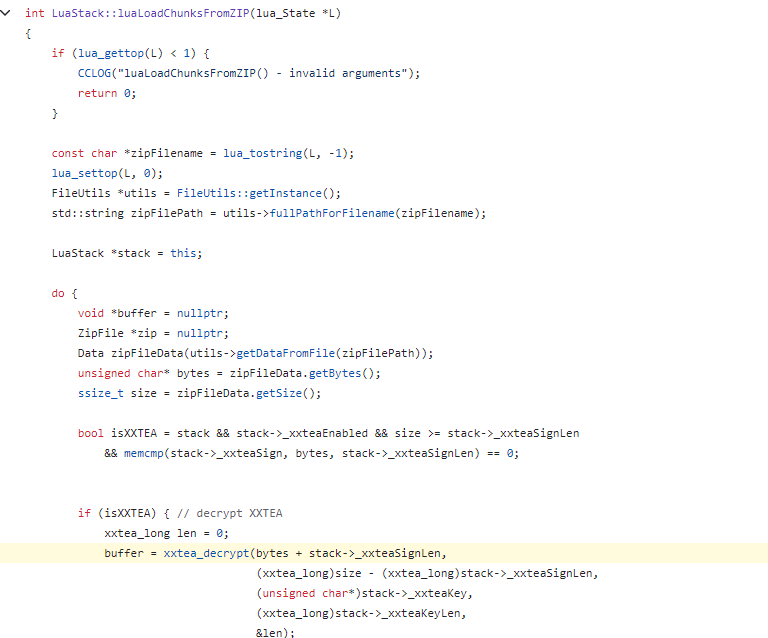
向上跟會發現它的bytes數據是由getDataFromFile函數獲取
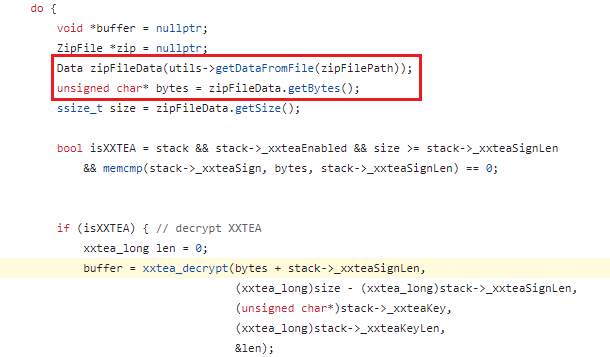
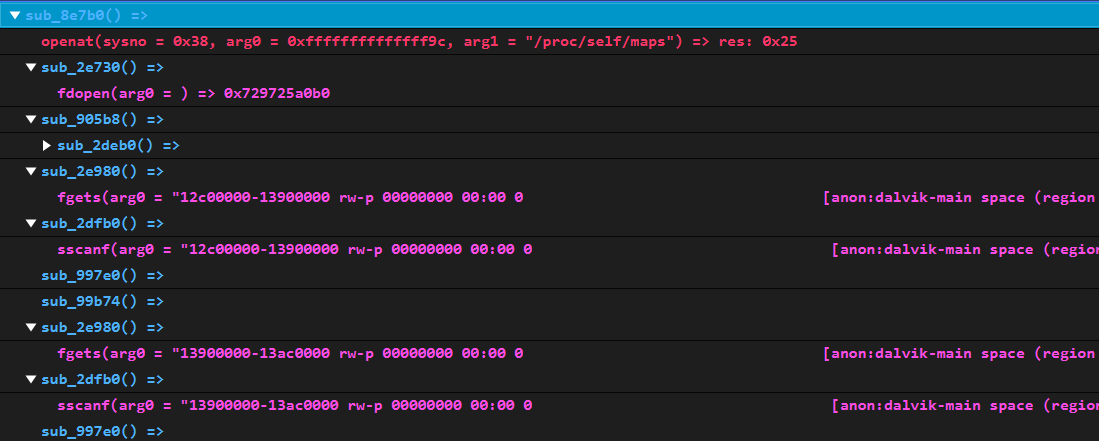
繼續跟getDataFromFile的邏輯,它會調用getContents,而getContents裡是調用fopen來打開,但奇怪的是hook fopen卻沒有發現它有打開任何.jsc文件
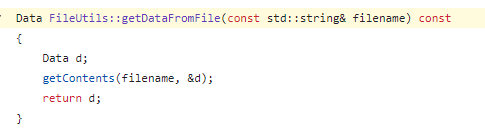
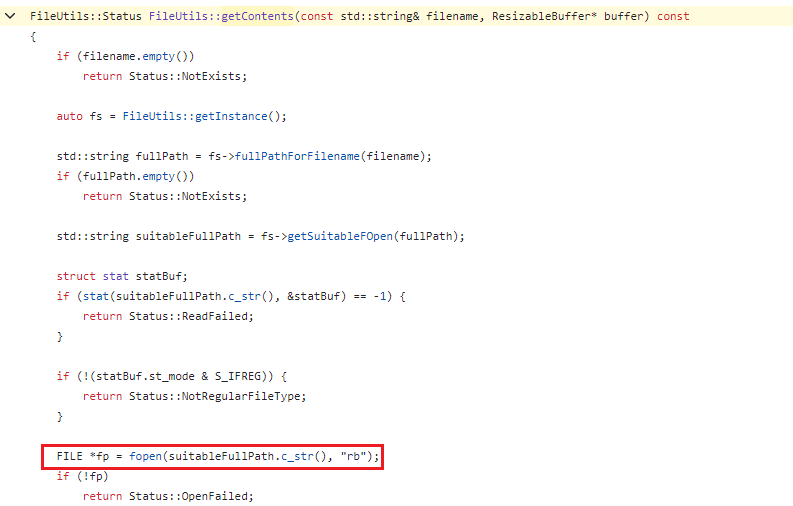
後來發現調用的並非FileUtils::getContents,而是FileUtilsAndroid::getContents。
它其中一個分支是調用libandroid.so的AAsset_read來讀取.jsc數據,調用AAssetManager_open來打開.jsc文件。
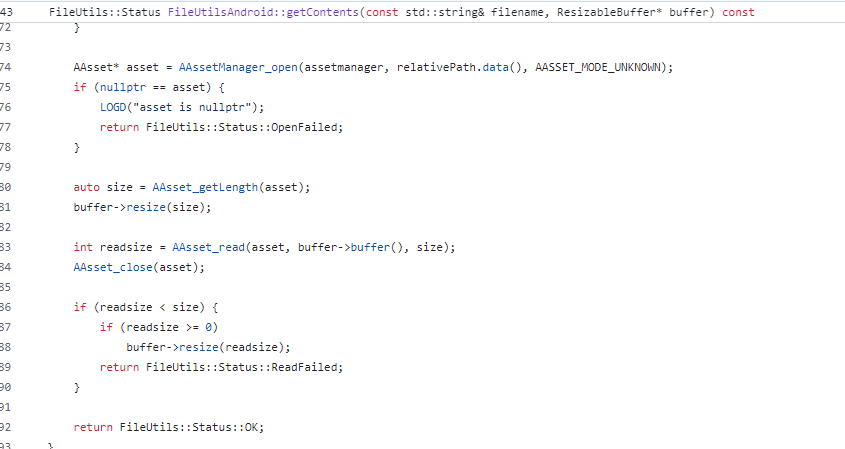
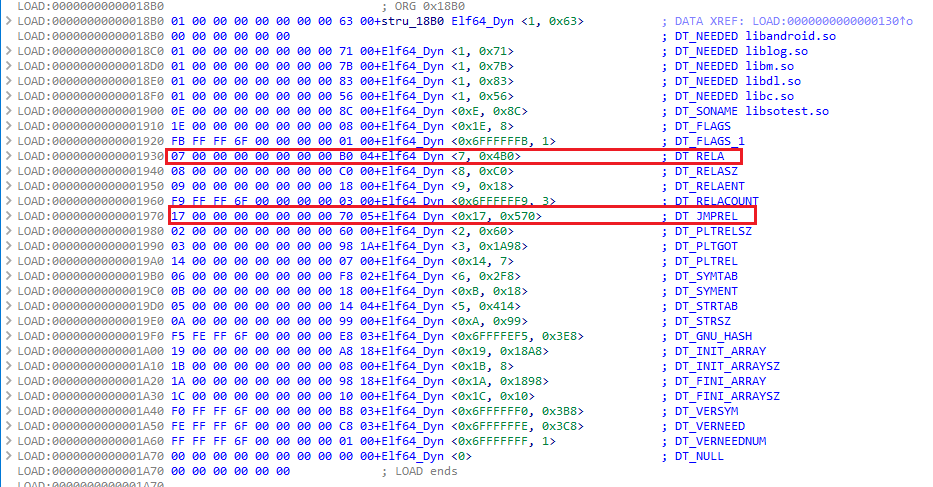
繼續對AAssetManager_open進行深入分析( 在線源碼 ),目的是找到能夠IO重定向的點:
AAssetManager_open裡調用了AssetManager::open函數
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
AAsset* AAssetManager_open(AAssetManager* amgr, const char* filename, int mode)
{
Asset::AccessMode amMode;
switch (mode) {
case AASSET_MODE_UNKNOWN:
amMode = Asset::ACCESS_UNKNOWN;
break;
case AASSET_MODE_RANDOM:
amMode = Asset::ACCESS_RANDOM;
break;
case AASSET_MODE_STREAMING:
amMode = Asset::ACCESS_STREAMING;
break;
case AASSET_MODE_BUFFER:
amMode = Asset::ACCESS_BUFFER;
break;
default:
return NULL;
}
AssetManager* mgr = static_cast<AssetManager*>(amgr);
Asset* asset = mgr->open(filename, amMode);
if (asset == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
return new AAsset(asset);
}
|
AssetManager::open調用openNonAssetInPathLocked
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
Asset* AssetManager::open(const char* fileName, AccessMode mode)
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
LOG_FATAL_IF(mAssetPaths.size() == 0, "No assets added to AssetManager");
String8 assetName(kAssetsRoot);
assetName.appendPath(fileName);
size_t i = mAssetPaths.size();
while (i > 0) {
i--;
ALOGV("Looking for asset '%s' in '%s'\n",
assetName.string(), mAssetPaths.itemAt(i).path.string());
Asset* pAsset = openNonAssetInPathLocked(assetName.string(), mode, mAssetPaths.itemAt(i));
if (pAsset != NULL) {
return pAsset != kExcludedAsset ? pAsset : NULL;
}
}
return NULL;
}
|
AssetManager::openNonAssetInPathLocked先判斷assets是位於.gz還是.zip內,而.apk與.zip基本等價,因此理應會走else分支。 奇怪的是當我使用frida hook驗證時,能順利hook到openAssetFromZipLocked,卻hook不到getZipFileLocked,顯然是不合理的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
Asset* AssetManager::openNonAssetInPathLocked(const char* fileName, AccessMode mode,
const asset_path& ap)
{
Asset* pAsset = NULL;
if (ap.type == kFileTypeDirectory) {
String8 path(ap.path);
path.appendPath(fileName);
pAsset = openAssetFromFileLocked(path, mode);
if (pAsset == NULL) {
path.append(".gz");
pAsset = openAssetFromFileLocked(path, mode);
}
if (pAsset != NULL) {
pAsset->setAssetSource(path);
}
} else {
String8 path(fileName);
ZipFileRO* pZip = getZipFileLocked(ap);
if (pZip != NULL) {
ZipEntryRO entry = pZip->findEntryByName(path.string());
if (entry != NULL) {
pAsset = openAssetFromZipLocked(pZip, entry, mode, path);
pZip->releaseEntry(entry);
}
}
if (pAsset != NULL) {
pAsset->setAssetSource(
createZipSourceNameLocked(ZipSet::getPathName(ap.path.string()), String8(""),
String8(fileName)));
}
}
return pAsset;
}
|
- 嘗試繼續跟剛剛hook失敗的
AssetManager::getZipFileLocked,它調用的是AssetManager::ZipSet::getZip。 同樣用frida hook getZip,這次成功了,猜測是一些優化移除了getZipFileLocked而導致hook 失敗。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
ZipFileRO* AssetManager::getZipFileLocked(const asset_path& ap)
{
ALOGV("getZipFileLocked() in %p\n", this);
return mZipSet.getZip(ap.path);
}
|
ZipSet::getZip會調用SharedZip::getZip,後者直接返回mZipFile。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
ZipFileRO* AssetManager::ZipSet::getZip(const String8& path)
{
int idx = getIndex(path);
sp<SharedZip> zip = mZipFile[idx];
if (zip == NULL) {
zip = SharedZip::get(path);
mZipFile.editItemAt(idx) = zip;
}
return zip->getZip();
}
ZipFileRO* AssetManager::SharedZip::getZip()
{
return mZipFile;
}
|
- 尋找
mZipFile賦值的地方,最終會找到是由ZipFileRO::open(mPath.string())賦值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
AssetManager::SharedZip::SharedZip(const String8& path, time_t modWhen)
: mPath(path), mZipFile(NULL), mModWhen(modWhen),
mResourceTableAsset(NULL), mResourceTable(NULL)
{
if (kIsDebug) {
ALOGI("Creating SharedZip %p %s\n", this, (const char*)mPath);
}
ALOGV("+++ opening zip '%s'\n", mPath.string());
mZipFile = ZipFileRO::open(mPath.string());
if (mZipFile == NULL) {
ALOGD("failed to open Zip archive '%s'\n", mPath.string());
}
}
|
方式二:從應用的數據目錄裡讀取
無論是方式一還是方式二,.jsc數據都是通過getDataFromFile獲取。而getDataFromFile裡調用了getContents。
1
| getDataFromFile -> getContents
|
在方式一中,我一開始看的是FileUtils::getContents,但其實是FileUtilsAndroid::getContents才對。
只有當fullPath[0] == '/'時才會調用FileUtils::getContents,而FileUtils::getContents會調用fopen來打開.jsc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
FileUtils::Status FileUtilsAndroid::getContents(const std::string& filename, ResizableBuffer* buffer) const
{
static const std::string apkprefix("assets/");
if (filename.empty())
return FileUtils::Status::NotExists;
string fullPath = fullPathForFilename(filename);
if (fullPath[0] == '/')
return FileUtils::getContents(fullPath, buffer);
}
|
替換思路
正常來說有以下幾種替換腳本的思路:
- 找到讀取
.jsc文件的地方進行IO重定向。
- 直接進行字節替換,即替換
xxtea_decypt解密前的.jsc字節數據,或者替換xxtea_decypt解密後的明文.js腳本。 這裡的替換是指開闢一片新內存,將新的數據放到這片內存,然後替換指針的指向。
- 直接替換apk裡的
.jsc,然後重打包apk。
- 替換js明文,不是像
2那樣開闢一片新內存,而是直接修改原本內存的明文js數據。
經測試後發現只有1、3、4是可行的,2會導致APP卡死( 原因不明??? )。
思路一實現
從上述可知第一種.jsc讀取方式會先調用ZipFileRO::open(mPath.string())來打開apk,之後再通過AAssetManager_open來獲取.jsc。
hook ZipFileRO::open看看傳入的參數是什麼。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| function hook_ZipFile_open(flag) {
let ZipFile_open = Module.getExportByName("libandroidfw.so", "_ZN7android9ZipFileRO4openEPKc");
console.log("ZipFile_open: ", ZipFile_open)
return Interceptor.attach(ZipFile_open,
{
onEnter: function (args) {
console.log("arg0: ", args[0].readCString());
},
onLeave: function (retval) {
}
}
);
}
|
可以看到其中一條是當前APK的路徑,顯然assets也是從這裡取的,因此這裡是一個可以嘗試重定向點,先需構造一個fake.apk push 到/data/app/XXX/下,然後hook IO重定向到fake.apk實現替換。

對我自己編譯的Demo而言,無論是以apktool解包&重打包的方式,還是直接解壓縮&重壓縮&手動命名的方式來構建fake.apk都是可行的,但要記得賦予fake.apk最低644的權限。
以下是我使用上述方法在我的Demo中實踐的效果,成功修改中心的字符串。
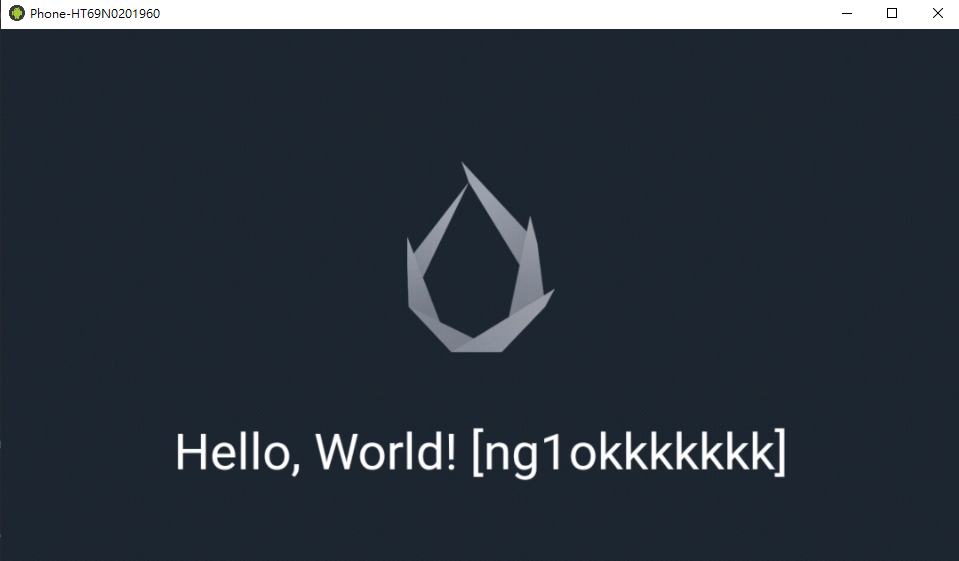
但感覺這種方式的實用性較低( 什至不如直接重打包… )
思路二嘗試(失敗)
連這樣僅替換指針指向都會導致APP卡死??
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| function hook_xxtea_decrypt() {
Interceptor.attach(Module.findExportByName("libcocos2djs.so", "xxtea_decrypt"), {
onEnter(args) {
let jsc_data = args[0];
let size = args[1].toInt32();
let key = args[2].readCString();
let key_len = args[3].toInt32();
this.arg4 = args[4];
let target_list = [0x15, 0x43, 0x73];
let flag = true;
for (let i = 0; i < target_list.length; i++) {
if (target_list[i] != Memory.readU8(jsc_data.add(i))) {
flag = false;
}
}
this.flag = flag;
if (flag) {
let new_size = size;
let newAddress = Memory.alloc(new_size);
Memory.protect(newAddress, new_size, "rwx")
Memory.protect(args[0], new_size, "rwx")
Memory.writeByteArray(newAddress, jsc_data.readByteArray(new_size))
args[0] = newAddress;
}
},
onLeave(retval) {
}
})
}
|
思路四實現
參考這位大佬的文章可知cocos2djs內置的v8引擎最終通過evalString來執行.jsc解密後的js代碼。
在正式替換前,最好先通過hook evalString的方式保存一份目標js( 因為遊戲的熱更新策略等原因,可能導致evalString執行的js代碼與你從apk裡手動解密.jsc得到的js腳本有所不同 )。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| function saveJscode(jscode, path) {
var fopenPtr = Module.findExportByName("libc.so", "fopen");
var fopen = new NativeFunction(fopenPtr, 'pointer', ['pointer', 'pointer']);
var fclosePtr = Module.findExportByName("libc.so", "fclose");
var fclose = new NativeFunction(fclosePtr, 'int', ['pointer']);
var fseekPtr = Module.findExportByName("libc.so", "fseek");
var fseek = new NativeFunction(fseekPtr, 'int', ['pointer', 'int', 'int']);
var ftellPtr = Module.findExportByName("libc.so", "ftell");
var ftell = new NativeFunction(ftellPtr, 'int', ['pointer']);
var freadPtr = Module.findExportByName("libc.so", "fread");
var fread = new NativeFunction(freadPtr, 'int', ['pointer', 'int', 'int', 'pointer']);
var fwritePtr = Module.findExportByName("libc.so", "fwrite");
var fwrite = new NativeFunction(fwritePtr, 'int', ['pointer', 'int', 'int', 'pointer']);
let newPath = Memory.allocUtf8String(path);
let openMode = Memory.allocUtf8String('w');
let str = Memory.allocUtf8String(jscode);
let file = fopen(newPath, openMode);
if (file != null) {
fwrite(str, jscode.length, 1, file)
fclose(file);
}
return null;
}
function hook_evalString() {
Interceptor.attach(Module.findExportByName("libcocos2djs.so", "_ZN2se12ScriptEngine10evalStringEPKclPNS_5ValueES2_"), {
onEnter(args) {
let path = args[4].readCString();
path = path == null ? "" : path;
let jscode = args[1];
let size = args[2].toInt32();
if (path.indexOf("assets/script/index.jsc") != -1) {
saveJscode(jscode.readCString(), "/data/data/XXXXXXX/test.js");
}
}
})
}
|
利用Memory.scan來找到修改的位置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| function findReplaceAddr(startAddr, size, pattern) {
Memory.scan(startAddr, size, pattern, {
onMatch(address, size) {
console.log("target offset: ", ptr(address - startAddr))
return 'stop';
},
onComplete() {
console.log('Memory.scan() complete');
}
});
}
function hook_evalString() {
Interceptor.attach(Module.findExportByName("libcocos2djs.so", "_ZN2se12ScriptEngine10evalStringEPKclPNS_5ValueES2_"), {
onEnter(args) {
let path = args[4].readCString();
path = path == null ? "" : path;
let jscode = args[1];
let size = args[2].toInt32();
if (path.indexOf("assets/script/index.jsc") != -1) {
let pattern = "76 61 72 20 65 20 3D 20 64 2E 50 6C 61 79 65 72 41 74 74 72 69 62 75 74 65 43 6F 6E 66 69 67 2E 67 65 74 44 72 65 61 6D 48 6C 70 65 49 74 65 6D 44 72 6F 70 28 29 2C";
findReplaceAddr(jscode, size, pattern);
}
}
})
}
|
最後以Memory.writeU8來逐字節修改,不用Memory.writeUtf8String的原因是它默認會在最終添加'\0'而導致報錯。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| function replaceEvalString(jscode, offset, replaceStr) {
for (let i = 0; i < replaceStr.length; i++) {
Memory.writeU8(jscode.add(offset + i), replaceStr.charCodeAt(i))
}
}
function cheatAutoChopTree(jscode) {
let replaceStr = 'true || " "';
replaceEvalString(jscode, 0x3861f6, replaceStr)
}
|
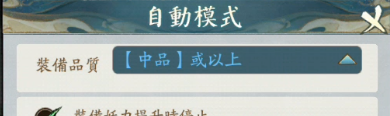
某砍樹手遊實踐
以某款砍樹遊戲來進行簡單的實踐。
遊戲有自動砍樹的功能,但需要符合一定條件

如何找到對應的邏輯在哪個.jsc中?直接搜字符串就可以。
利用上述替換思路4來修改對應的js判斷邏輯,最終效果:
結語
思路4那種替換手段有大小限制,不能隨意地修改,暫時還未找到能隨意修改的手段,有知道的大佬還請不嗇賜教,有任何想法也歡迎交流^^

















/Untitled.png)
/image3.png)
/image.png)