2025吾愛解題領紅包活動(Android題解)
前言
簡單寫一下Android部份的解題思路。
第三題:Android初級題
明顯的xxtea特徵。
/image.png)
/image1.png)
解密後直接得到flag
/image2.png)
/image3.png)
第四題:Android中級題
目標是找到秘鑰。
/image4.png)
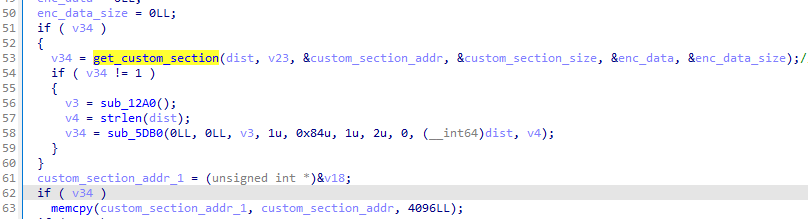
Java層關鍵邏輯如下,調用了Check函數來檢查密鑰。
/image5.png)
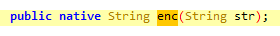
是個native函數。
/image6.png)
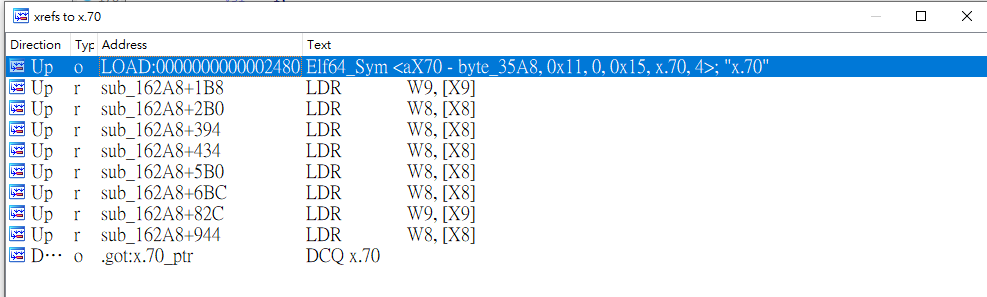
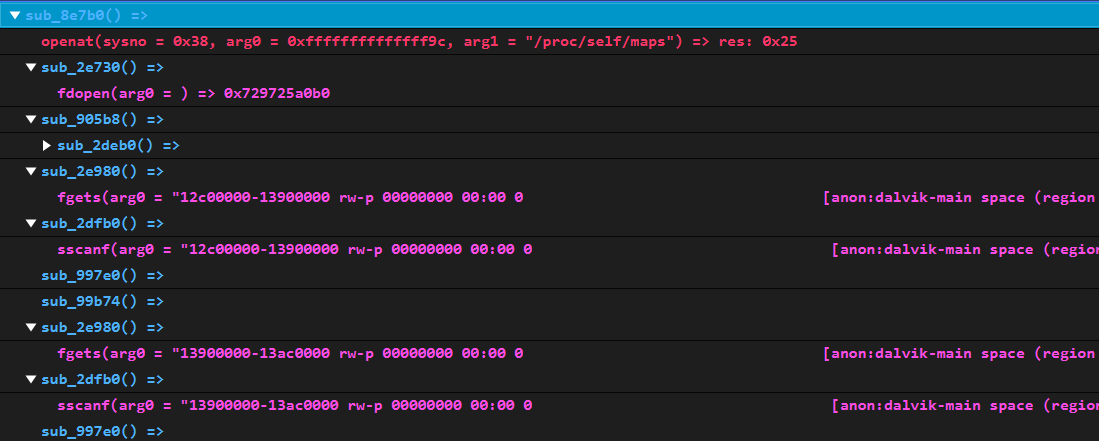
嘗試直接hook RegisterNatives,發現Check果然是動態注冊的,在0xe8c54。
/image7.png)
Check一開始是一些反調試邏輯。
/image8.png)
先看anti1,它調用decrypt_str解密字符串,但奇怪的是解密出來的字符串不是以\x00結尾,導致opendir直接失敗,使得後面的反調試邏輯形同虛設?( 不知是故意的還是不小心的 )
/image9.png)
anti2、do_something1也同理,皆因為decrypt_str的問題導致後續的邏輯失效。
繼續向下跟,看到它動態計算出一個函數地址,大概率就是加密函數,最後與密文進行對比。
一開始以為動態計算的那個函數地址是固定的,後來才發現有兩個不同的地址,會隨著上面anti1、anti2、do_something1、getenv等函數返回的結果而改變。
類似蜜罐的概念,當觸發anti邏輯後,不主動殺死APP,而是改變程序的執行流,導向錯誤的分支。
/image10.png)
func1、func2如下,前者是錯誤的分支,後者是正確的,我的環境默認會走func1。
可以看到兩者的加密方式都是相同的異或加密,不同的只有異或的值。
/image11.png)
/image12.png)
經測試發現,手動hook getenv、do_something1修改其參數、返回值後,程序才會走向func2。這時再hook encrypt,將正確的異或值dump下來。
1 | function hook_dlopen(soName) { |
最終解密腳本:
1 | xor_key1 = [0x2E, 0x4B, 0xEE, 0xC8, 0xE0, 0x95, 0x88, 0x47, 0xB0, 0x72, 0x1B, 0x68, 0x40, 0xD0, 0x0A, 0x84] |
輸出:flag: flag{md5(uid+2025)}
第六題:Windows & Android高級題
Java層分析
先看看題目描述,要幾個重點:
- flag格式為
flag{XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX},其中X要麼是大寫字母,要麼是數字。 - 不同UID對應不同的Flag,可能有多個解。
- SISC中的S意為堆棧。
/image13.png)
再看看APP,要求輸入UID和Flag。
/image14.png)
用新版jeb查看Java層邏輯( Java層有混淆,jeb能忽略部份混淆,方便分析 ),發現調用check函數來檢查,參考分別是UID和Flag。
/image15.png)
check是Native函數。
/image16.png)
vm初始化
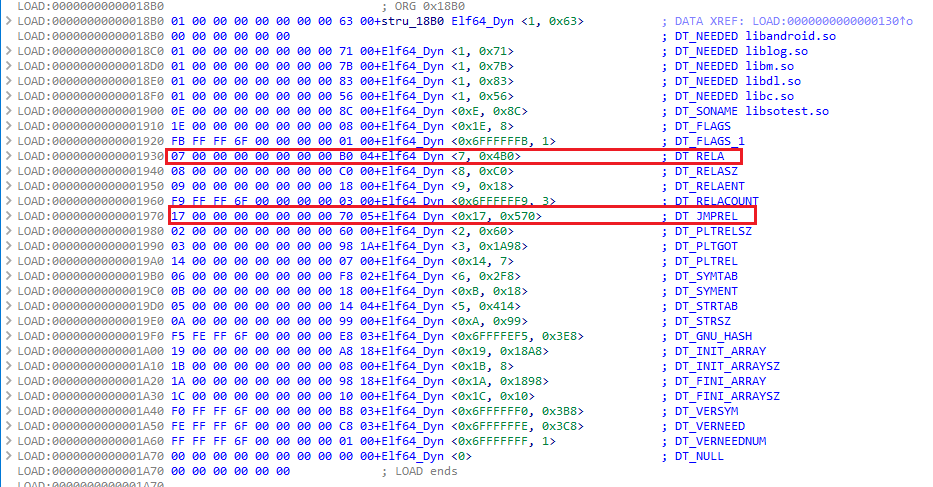
native層的check是靜態注冊的,能直接搜到。
/image17.png)
繼續深入分析( 配合動調來遂一分析每個函數的作用 )。
/image18.png)
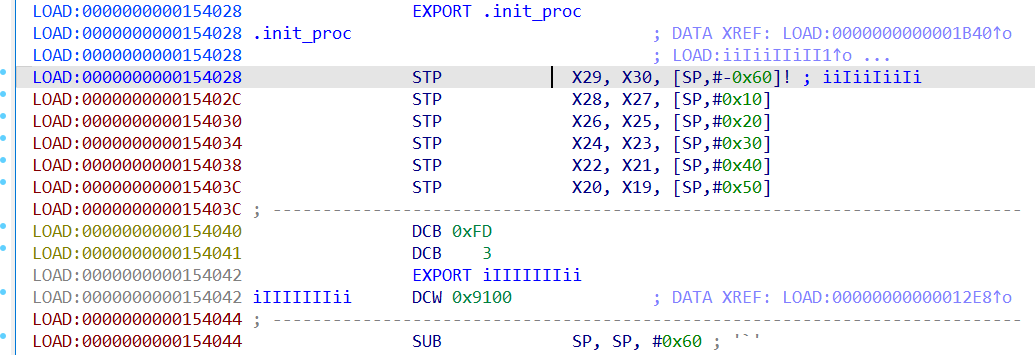
init_some_data函數如下,結合後面的分析可以知道,這裡是在初始化vm虛擬機的opcodes,存放在a1[0xC000 ~ 0xC200]。
將a1記為vm_ctx,意指vm虛擬機的上下文空間。
/image19.png)
start_vm
初始化完成後便會調用start_vm正式啟動虛擬機進行計算。
一開始會通過一些運算獲取_opcode和arg,前者是操作碼、後者是一些固定的參數( 在不同的操作碼中都有不同的含義 )。
/image20.png)
接著就是vm最經典的一大段switch,每個case對應不同的handler,實現了不同的功能。
每個handler裡基本上都會用到vm_ctx[0x10002],一些參數、中間值、計算結果都會存放在vm_ctx[0x10002]指向的位置。
而且可以看到vm_ctx[0x10002] + 4、vm_ctx[0x10002] - 4等等的運算,再結合題目的描述,可以猜測vm_ctx[0x10002]相當於sp( 棧指針 ),該虛擬機的所有運算操作都會在它自己維護的棧中進行( 沒有寄存器的概念 )。
/image21.png)
vm handler分析與還原
大部份handler的實現都比較簡單,配合動調很容易就可以分析出來。
記錄幾個沒那麼容易看出來的handler。
handler7:&v26[-arg]相當於&v26 - arg,這裡是在將棧頂元素與棧頂後arg個元素交換。
/image22.png)
handler22:注意_pc += (char)arg,對應匯編是ADD W11, W11, W12,SXTB,其中SXTB是對W12的修飾符,表示將W12的最低8位進行符號擴展,在還原handler時要特別留意這一點。
/image23.png)
花億點時間,還原所有handler,實現一個簡單的vm解釋器:
1 | def write_mem_str(addr, content): |
提醒:flag格式為flag{XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX},其中X要麼是大寫字母,要麼是數字。
腳本中的測試flag要記得符合這個格式,腳本的輸出日志記為vm.log。
加密邏輯分析
前置:在動調的過程中發現handler26會獲取輸入的Flag,加密邏輯大概會在那附近。
在vm.log中搜h26_getinput定位到相關位置,首先判斷了input是否flag{ }的格式。
1 | [h26_getinput] pop, *sp = vm_ctx[0x1000 + 0x0] = 0x66 # 'f' |
從input[5]開始才是真正的內容,對input[5~8]的運算可以總結為:查表、自減、乘0x24。
1 | # 處理input[5] |
對input[9]有特別的處理,查表、自減操作仍舊保留,不同的是後面會判斷tmp >> 25是否不為0,若是則進行自加、取餘操作。
取餘操作中的模數,會根據輸入的UID不同而變化,即固定UID對應固定的模數。
( 注:以-分隔的每組字串的最個一個元素都是這樣處理的 )
1 | # 以下日志不是連續的, 為了好看將其放在一起 |
以-作為分隔符,每組處理完後會以|來融合。
1 | [h4_orr] pop, *sp = 0x1fc3d5 | 0x8a1245 = 0x9fd3d5 |
最後會自減、異或0xc15303fb,這個值是固定的。
1 | [h30_sub1] *sp = *sp - 1 = 0x19fffff - 1 = 0x19ffffe |
綜合上述分析,可以大概用Python還原出加密邏輯:
1 | tables = [0x09, 0x0A, 0x10, 0x15, 0x21, 0x13, 0x0C, 0x04, 0x11, 0x1C, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x03, 0x0F, 0x20, 0x0D, 0x02, 0x23, 0x06, 0x1B, 0x14,0x0E, 0x01, 0x16, 0x19, 0x08, 0x12, 0x1F, 0x17, 0x24, 0x0B, 0x1E, 0x07, 0x1A, 0x05, 0x18, 0x1D, 0x22, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00] |
最終解密
基於上述加密腳本,似乎無法直接反推出對應的解密邏輯,而且題目描述中提到有多個解也認證了這一點。
密文是0x3EACFC04,(0x3EACFC04 ^ 0xc15303fb) == 0xFFFFFFFF,而-1的16進制正是該值,因此只要在最終的自減前,res的值為0,即可滿足等式。
/image24.png)
上面提到,以-分隔的每個字串的最個一個元素都會進行取餘的操作( 前提是>>25不為0 ),這一步就可以很方便讓tmp歸0。
以-分隔的每組數據計算過程如下,現在的目標是讓tmp等於0,因此d + input_[4]必須是target的整數倍。
此時問題轉化為如何讓d + input_[4] == n * target,其中n、target都是已知的。
( 注:input_[i]指input[i]查表後的結果、target是每組的模數 )
1 | a = (input_[0] - 1) * 0x24 |
以下腳本用來求input_[0 ~ 4]這幾個未知量( 初始為0 ),原理如下:
- 先爆破
input_[0],若input_[0]為i會使func函數返回值>0且input_[0]為i+1會使func函數返回值<0,則代表i就是input_[0]的最大值,也是input_[0]其中一個可能的值。 - 確定了
input_[0]後,用同樣方法確定input_[1 ~ 4]。 - 最終可以確定
input_[0 ~ 4],由此反查tables來確定input[0 ~ 4]字符串。
注:當input_[j]被確定為0時,是不合理的,要將input_[j - 1] -= 1,然後再重新計算input_[j]的最大值。
1 | # tables的範圍為 (0x0, 0x24] |
運行腳本得到一個可行的Flag為HB0P6-Y84V7-YSWDH-9RZPB:
/image25.png)
第八題:Android高級題
直接hook RegisterNatives,看到flag驗證邏輯在lib52pojie.so!0x134d4。
1 | [RegisterNatives] java_class: com.wuaipojie.crackme2025.MainActivity name: checkSn sig: (Ljava/lang/String;)Z |
看到一堆~、^、|操作,但其實它們並非加密邏輯,而是類似ollvm裡的「指令替換」混淆,也叫MBA表達式。
簡單來說就是將一段很簡單的指令( 如a + b ),通過疊加~、^、|等操作符轉換成完全等價的複雜指令。
/image26.png)
由於沒有解混淆的思路,因此只能直接動調慢慢看邏輯。
調用get_input_8取了input的一部份,然後傳入encrypt。
/image27.png)
encrypt中主要分成3部份,先看encrypt_part1。
/image28.png)
encrypt_part1
input.n128_u64[0]是低64位,代表傳入的flag,input.n128_u64[1]是高64位,用來存放結果。
只看與input有關的,hook發現input.n128_u64[0]每輪固定左移-1,即右移1。
由此得出input.n128_u64[0]的迭代方式:input = (input >> 1) & (2 ** 64 - 1)
/image29.png)
input.n128_u64[1]只與tmp1有關。
/image30.png)
/image31.png)
frida stalker打印tmp1、input_1.n128_u64[1]+=的那個值,發現要將tmp1看成2進制位,每輪都會拼到input_1.n128_u64[1]的低位。
即input1 = (input1 << 1) | tmp1,而tmp1其實就是取input.n128_u64[0]的最低位。
1 | [2] x26: 0x1 x27: 0x3332317b67616c66 |
最終encrypt_part1可以簡化為:
1 | def encrypt_part1(input): |
encrypt_part2
encrypt_part2的邏輯比encrypt_part1複雜得多,繼續像上面那樣分析實在不太理智( 有心無力 ),本來都打算放棄了,結果當天晚上吾愛放出了提示:
1 | 2025.02.10 16:45 【春节】解题领红包之八 {Android 高级题} 对称算法,需要识别出算法类型,找出初始化后的密钥后反推即可,对应获取奖励也减半 |
對稱算法,結合分析過程中看到的一些表,嘗試直接搜看看表中的數據。
/image32.png)
發現其實是DES算法。
/image33.png)
而且根據提示,密鑰是初始化過的。
hook encrypt,打印args[0],發現每個QWORD剛好都是6字節大小的數據,而DES算法的round key也是48位,因此這大概率就是提示所述的初始化過的密鑰。
/image34.png)
算法分析
DES算法:https://blog.csdn.net/nicai_hualuo/article/details/123135670
基於原版DES,遂步分析,還原到最後發現其實是3DES。完整腳本如下:( 腳本是其於上述文章改的 )
1 |
|
輸出flag:
1 | flag: 52PojiEHaPpynEwY3ar2025! |
/Untitled.png)
/image3.png)
/image.png)